Phenylketonuria And Nutrition

Also known as PKU, phenylketonuria is a disease caused by a congenital error in the metabolism of an amino acid. The progression and effects derived from this disease depend on the moment of diagnosis; the sooner it occurs, the better.
Congenital metabolic diseases
This group of diseases, which includes phenylketonuria, are due to genetic alterations. The alteration of a gene produces an enzymatic defect that causes the accumulation of toxic metabolites. Most of these diseases appear in early childhood, but their appearance and symptoms are highly variable.
Many of the inborn errors of metabolism respond to nutritional treatment. The objectives of this are to reduce the accumulation of the toxic compound and supply the deficiencies of nutrients and micronutrients that may appear secondary to the pathology.
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is characterized by an accumulation of an amino acid in the blood, phenylalanine. Its early diagnosis is essential, since the effects of excess phenylalanine (mental and psychomotor retardation) are irreversible. For this reason, it has been included in neonatal screening programs since the 20th century, despite having a low incidence.

Clinical management of phenylketonuria
The goal of treatment is to maintain adequate phenylalanine concentrations to support growth and development during all stages of the life cycle. The degree of intervention will depend on the level of residual activity of the enzyme, therefore, the approach must be individual. Although the main management is nutritional, there are also other treatments.
Dietary treatment
It is the primary treatment. Regardless of the degree of tolerance, as it is a disease in which proteins must be controlled, some general principles must be observed.
- Long periods of fasting will be avoided.
- Total protein provided with food will be restricted in order to limit the phenylalanine content of the diet. This amount will vary depending on individual tolerance. To guarantee protein needs, special phenylalanine-free formulas will be used.
- It is important to ensure adequate caloric intake, calculated based on age, weight and gender, in order to achieve adequate growth.
- You cannot forget the basic principle of any dietary guideline: variety. The diversity of foods and cooking techniques favors adherence. In addition, there are special low-protein products valid for these patients.
Applying concepts
To make a diet restricted in phenylalanine, you have to limit foods rich in protein, in general, and in this amino acid, in particular. Before talking about restrictions, we will specify what can be consumed.
Foods allowed for phenylketonuria
The vegetables, fruits and vegetables can be consumed in a less controlled manner. You can take advantage of these foods to diversify your diet as much as possible. Other products that can be consumed because they are low in phenylalanine are cornstarch and tapioca. The use of cornstarch is very common in celiac patients and there are multiple recipes in which it can be incorporated.
When cooking, vegetable fats and oils can be used, always prioritizing virgin olive oil. However, within the fats, butter, margarines that do not contain milk, tallow and lard are allowed.
Finally, there is another wide range of products that you can consume, although some are not so recommended. Sugar, jam, honey, and syrup can be eaten, as can spices and condiments, such as vinegar and mustard. With regard to drinks, although water must always be the main source of hydration, soft drinks are suitable for these people.
Foods to control
The list of forbidden foods is quite extensive, but, as mentioned at the beginning, tolerance varies from one person to another. Normally, they tend to tolerate small amounts of protein, so developing tables of equivalences usually facilitate the flexibility of the diet.
For example, 25 grams of whole milk contains 50 milligrams of phenylalanine. So if a person tolerates 600 milligrams of phenylalanine per day and has equivalence tables, he can vary and adjust the diet himself.
Apart from protein foods, they are restricted in the consumption of normal bread, flours and cookies. There is a range of special low-protein products, known as PKU, that can be found online.
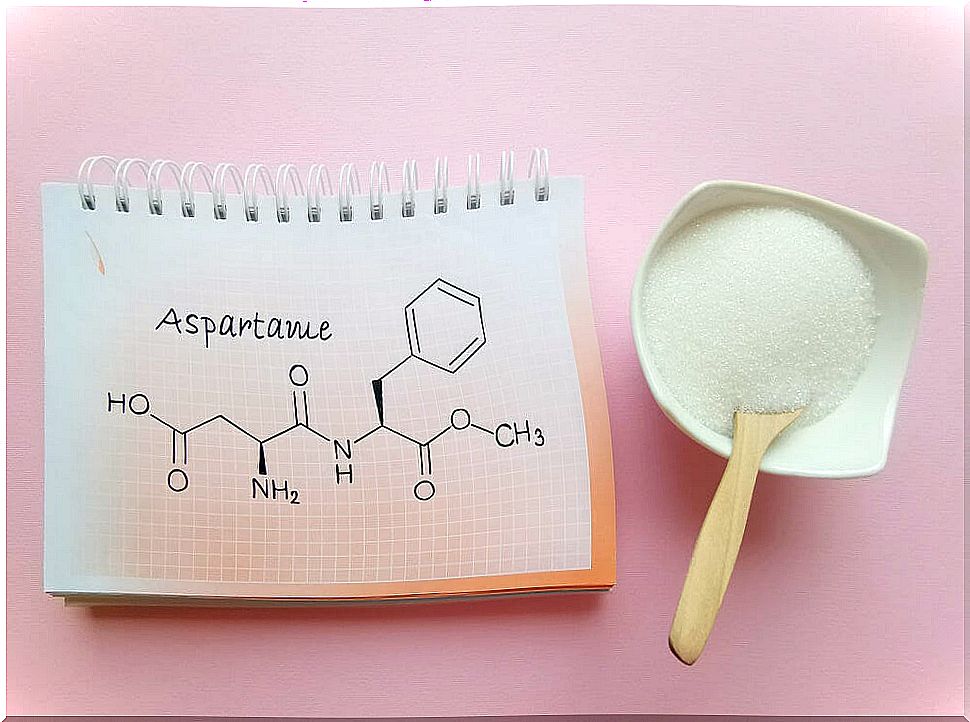
In addition, all light , zero or low calorie drinks or products are contraindicated because they contain one of the most popular sweeteners: aspartame.
Thus, on the following website they collect a wide variety of recipes adapted to patients with phenylketonuria and many tips in this regard.