Can I Get Pregnant If I Have A Tubal Ligation?
The tubal ligation procedure is a fairly common sterilization method. However, like any surgical process it raises doubts and even more so when it comes to contraception. Being tubal tied implies that we have decided to end our reproductive faculty almost permanently. Although it is considered an effective sterilization mechanism, it is known to be a risky method.
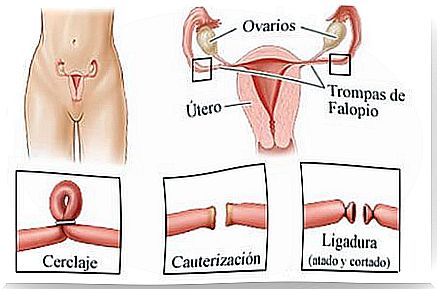
Tubal ligation applies to those women who have decided not to have more children, because it is a permanent method. It is a simple and outpatient procedure, which can be done in different ways. A woman can schedule her ligation for any day, even at the time of delivery.
Currently there are techniques that allow surgery to be performed via laparoscopy, one of the simplest. Through this surgical process , the passage of the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus is prevented. The cauterized tube ends have a long-lasting effect, but sometimes the procedure fails.
Is tubal ligation permanent?
This method cannot be considered as reversible or temporary, so it is important to plan it well. It is taken into account by those women who do not want to become pregnant in the future. In addition, it is also recommended for those who are over 40 and have a history of ovarian cancer.
It is understood that many women have regretted the decision to undergo this surgery, especially because of its effectiveness. However, it is also known that one in two hundred women can become pregnant again after having their tubes tied. In other words, the process is not definitive, even though the incidence rates are actually very low.
So, it is not enough to just have this surgery and assume that we will never have to take care of getting pregnant again. Specialists recommend monitoring to establish the evolution of the procedure, as there are other risks. According to the data, a woman who undergoes this intervention, in addition to having a probability of pregnancy in the future, is also exposed to the following.
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy
- Incomplete closure of the tubes (in case of hysteroscopic procedure)
- Damage to tissues or organs adjacent to the surgical area, in this case as a result of contact with the surgical material
- Consequences of general anesthesia
- Pain from build-up of surgical gas
- Anomaly in the menstrual cycle
When the intervention is performed through the hysteroscope, the specialists recommend that the woman continue using an alternative contraceptive method, until verifying the success of the intervention. In this case, an evaluation called hysterosalpingography is scheduled, which is performed three months after the intervention.
Similarly, it is possible to reverse the intervention, through a procedure called recanalization. Recanalization is also performed surgically and consists of clearing the tubal canal again. When recanalization is performed, the chances of pregnancy are restored, only this time the in vitro fertilization process is recommended.
How do you know if the tubal ligation has worked?
Our doctor will always be able to make an evaluation that allows him to tell us how everything is going. For example, in the event that the channel has not been completely closed, it may warn us of the risk. If necessary, we may receive an indication to continue taking contraceptives or any other option to proceed.
In the event that we are from the group that regretted the procedure, some tests will shed light on our condition. The reversal of the intervention is believed to apply as long as the endings closest to the ovary remain intact. For this, it is necessary that there is a length of at least 4 cm of channel in operation.
However, if the tube has been completely removed, reversal may be considered impossible. Similarly, over the years, a greater risk of pregnancy is considered in the case of tubal ligation. In this sense, statistically we speak of probabilities of 1 in 1000 during the first year, but it increases between 2 and 10 of every thousand after the five years of the intervention.