How To Explain The Cell To Children

In order to explain the cell to children, it is important that before we can answer some questions such as: “What are cells?” or “How can we explain the cell concept to children?”
All the living creatures are formed from cells. There are two types: prokaryotes, whose genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm, and eukaryotes, with a defined nucleus that contains the genes. On this basis, we will try to answer the questions posed.
What is the origin of the word cell?
In 1965, Robert Hooke (1635-1703), an English scientist, observed a fragment of cork under a rudimentary microscope. He discovered that it was made up of a series of structures similar to the cells of the honeycombs of bees and called these cavities cells. What he was really seeing were dead plant cells with a polyhedral shape. Without knowing it, he laid the foundations of the Cell Theory.
What is a cell?
Matthias Schleiden (1804-1881) and Theodor Schwann (1810-1882) enunciated the Cell Theory in 1838 and 1839, respectively. The first for plant cells and the second for animal cells. The cell theory includes 3 postulates that characterize and define the cell :
- All organisms are cells or are made up of one or more cells.
- Every cell has the machinery necessary to keep itself alive.
- Every cell always comes from another cell. Cells are not created anew.
Later, with the discovery of DNA in the 1950s, a fourth postulate was added:
- Every cell contains hereditary material within it and is a genetic unit.
Definition of cell
According to the Cell Theory, we can summarize that the cell is the structural, physiological, reproductive and genetic unit of living beings. Or put another way: the cell has to fulfill 4 functions: anatomical, physiological, reproductive and hereditary.
How do we adapt the concept to explain the cell to children?
It is important that children feel comfortable when it comes to expressing themselves correctly using scientific language, so we should not look for synonyms for technicalities. The cell must be explained to children without losing scientific rigor. We must, therefore, help them understand and acquire scientific concepts and vocabulary through games and analogies in their daily lives.
We propose a couple of ideas that can help you explain the different types of organisms and the different structures of a eukaryotic cell.
Types of organisms: the example of blocks
Organisms can be unicellular, made up of a single cell that performs all vital functions, or multicellular, which is made up of many cells that perform different functions.
Let’s think of a game of different colored blocks. If each block alone can carry out the functions of relation, reproduction … it will itself constitute a unicellular organism such as, for example, a bacterium. All blocks of the same color, with the same characteristics, will belong to the same species.
If, on the contrary, we need blocks of different colors and shapes to build a figure, we will be talking about a multicellular organism, where the same blocks will represent the same cell type in charge of performing a certain function.
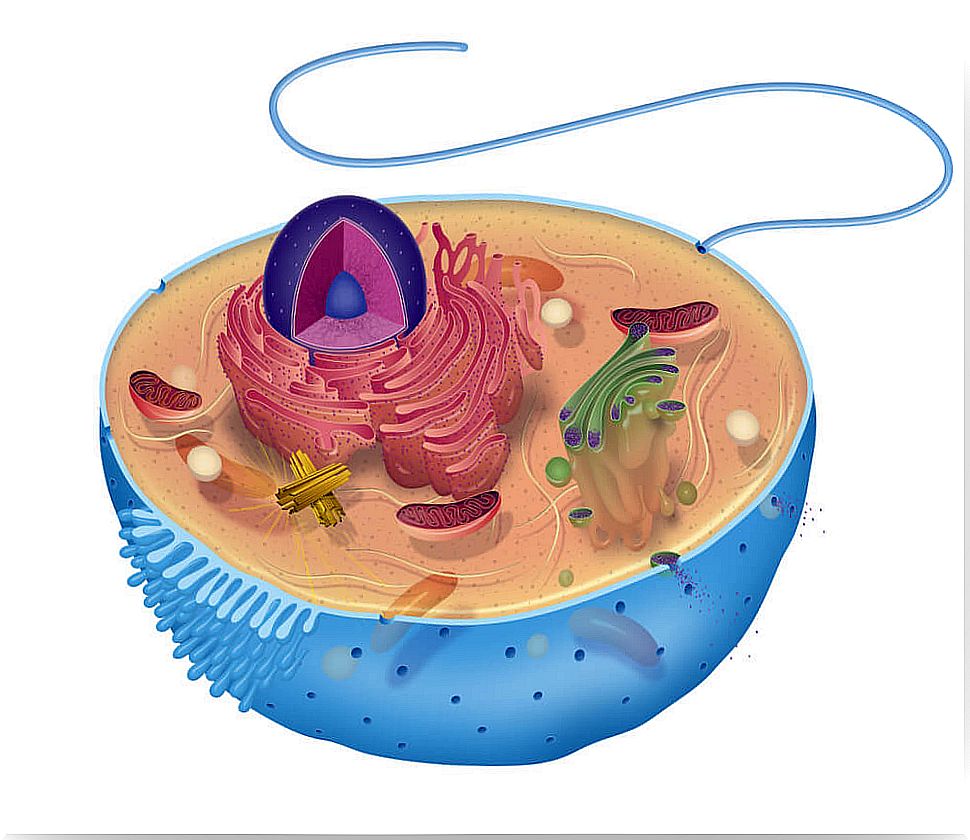
Parts of a eukaryotic cell: the egg analogy to explain the cell to children
What better way to be able to explain something if it is an image that speaks for itself. To do this, we will look for the largest cell we can find: an ostrich egg. Using the different parts of an egg as an analogy, we are going to see, from the outside to the inside, the different cellular structures:
- Cell wall (shell). Rigid covering that surrounds the plasma membrane. It is only present in plant cells.
- Plasma membrane (membrane that covers the shell). It is the layer that surrounds the cell. It protects it from the external environment, allows the passage of substances and the elimination of waste.
- Cytoplasm (clear). It is the liquid substance inside the cell. In it we find the organelles and the nucleus.
- Organelles There are several types and each one performs a different function. They are like the organs of a living being but of the cell.
- Nucleus (yolk). It is the most important organelle. Inside it is the hereditary material, which is what characterizes us.
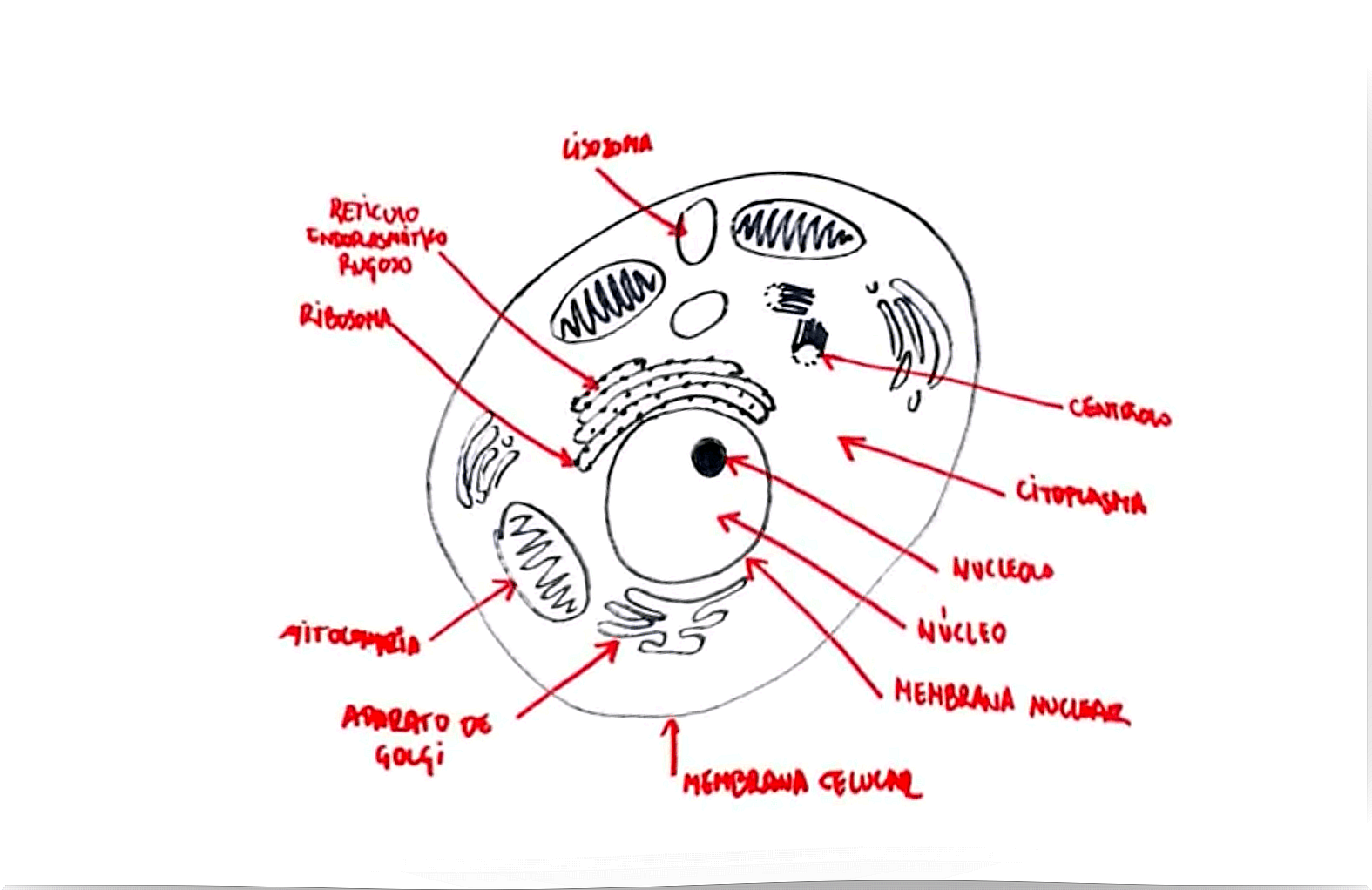
Drawing of an animal cell | YouTube: @DibuClases
When it is time to explain the cell to the children, we can support our explanation with a simple drawing that schematizes the parts of a cell. In this way, we reinforce not only content learning, but also visual and retentive memory. Thus, we will ensure that the main ideas of the subject remain in the memory of the medium and long term memory.