Respiratory Distress Syndrome In The Newborn
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), also known as respiratory distress or hyaline membrane disease, is a respiratory disorder that occurs especially in premature newborns.
What is respiratory distress syndrome?
Respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by a lack of surfactant or surfactant from the lungs and is linked to lung immaturity. Normally, this agent is produced from the 34th week of gestation.
But what is surfactant or surfactant? It is a liquid composed of lipids and proteins that allows the alveoli to remain open so that we can breathe. Its function is to reduce the surface tension and prevent them from closing when the air comes out.
In this way, when there is a deficiency of this surfactant, much greater pressure is required to open the alveoli with the entry of air. This causes an inflammation of the lungs and the possibility of the appearance of pulmonary edema. The blood is not oxygenated well and the availability of oxygen throughout the body decreases.
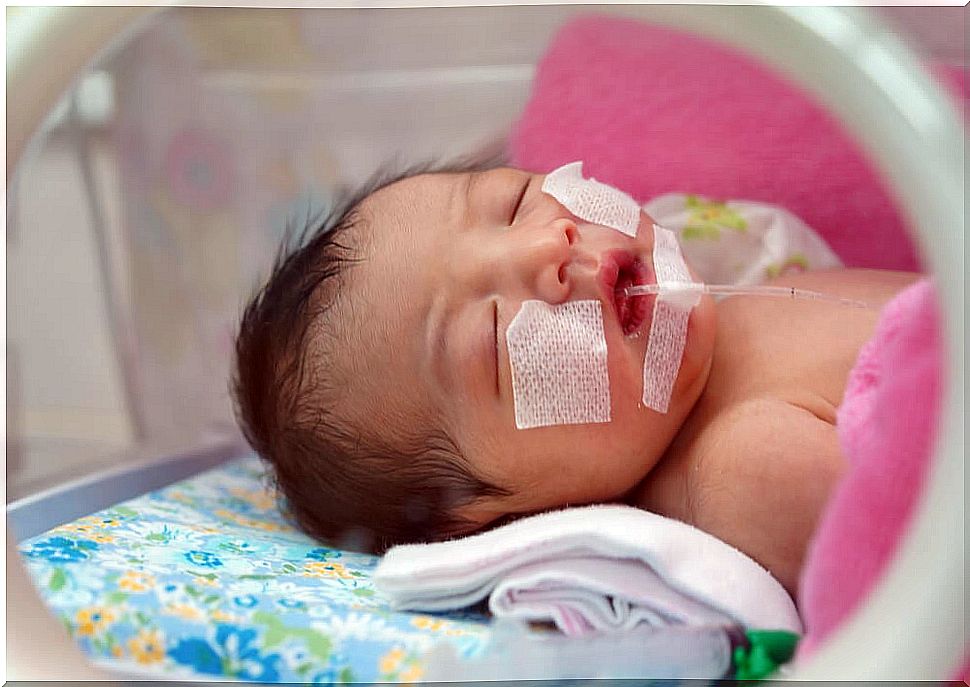
Respiratory distress syndrome is the fundamental cause of respiratory failure in premature newborns, especially those born before week 34. The risk increases the fewer weeks of gestation they are at birth.
Main risk factors
As we have said, the most important risk factor for respiratory distress syndrome is prematurity. In addition, other predisposing factors for the appearance of this syndrome are the following:
- Premature rupture of membranes.
- Induction of labor.
- Birth by cesarean section.
- Diabetic mother.
- Hemorrhage during childbirth.
- Multiple births.
- Meconium amniotic fluid.
Symptoms
The main symptoms that appear in a newborn with respiratory distress are:
- Costly moan breaths.
- Increased respiratory rate.
- Unusual movement of the pectoral muscles when breathing.
- Nasal flutter.
- Tachycardia.
- Cyanosis: bluish color of the skin.
Some of the possible complications that can arise if it is not treated properly are:
- Metabolic disorders
- Pulmonary deterioration.
- Hypotension
- Intracranial hemorrhages.
- Sepsis or infection.
- Pneumothorax: accumulation of air in the space that surrounds the lungs.
Treatment of respiratory distress syndrome
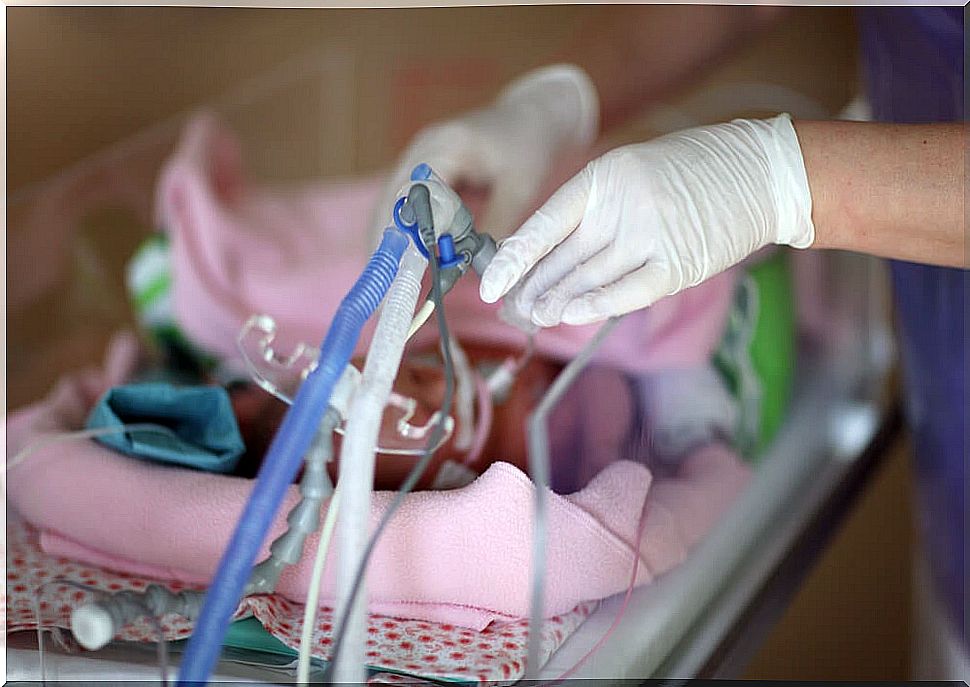
Classically, treatment has been based on administering surfactant or surfactant and applying mechanical ventilation. For this, endotracheal intubation is necessary.
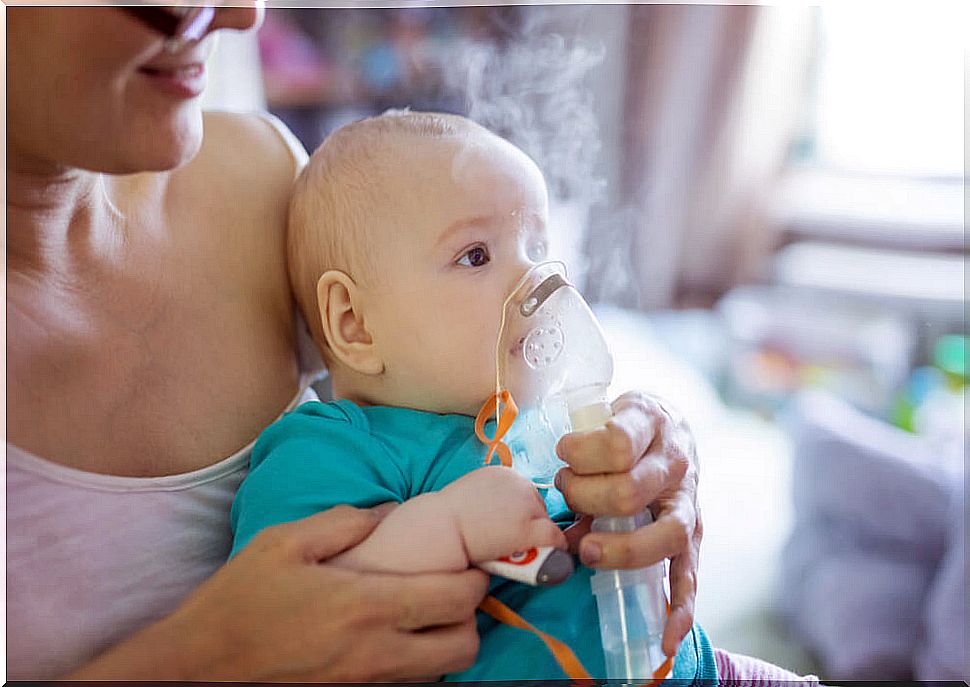

However, there are more and more supporters of the use of non-invasive ventilation. In this sense, the least affected newborns with a better prognosis, which are usually the largest or least premature, may simply require the application of oxygen, with continuous air pressure through the nose.
However, early application of artificial surfactant reduces lethality and complications. In addition, it is linked to a lower need for mechanical ventilation and intubation time.
The most commonly used artificial surfactants in these cases are:
- Beractant.
- Poractant alpha.
- Calfactant.
- Lucinactant.
Generally, with treatment, the prognosis is very good. The lungs, thanks to the ventilation, begin to produce the surfactant on their own and the process resolves in a few days.
How can it be prevented?
When labor is expected to be premature or preterm, glucocorticoids, such as betamethasone , are usually given to the mother. These help to mature the lungs of the fetus, accelerating the production of the surfactant.
In fact, before delivery, it is possible to assess the state of maturity of the lungs by analyzing the amniotic fluid. Thus, the risk of presenting respiratory distress at birth, among other complications , is reduced.
In either case, if possible, labor should try to be delayed until 39 weeks or until the lungs are considered mature. Preterm labor always has more associated risks that it is better to prevent.