Dry Skin In Children
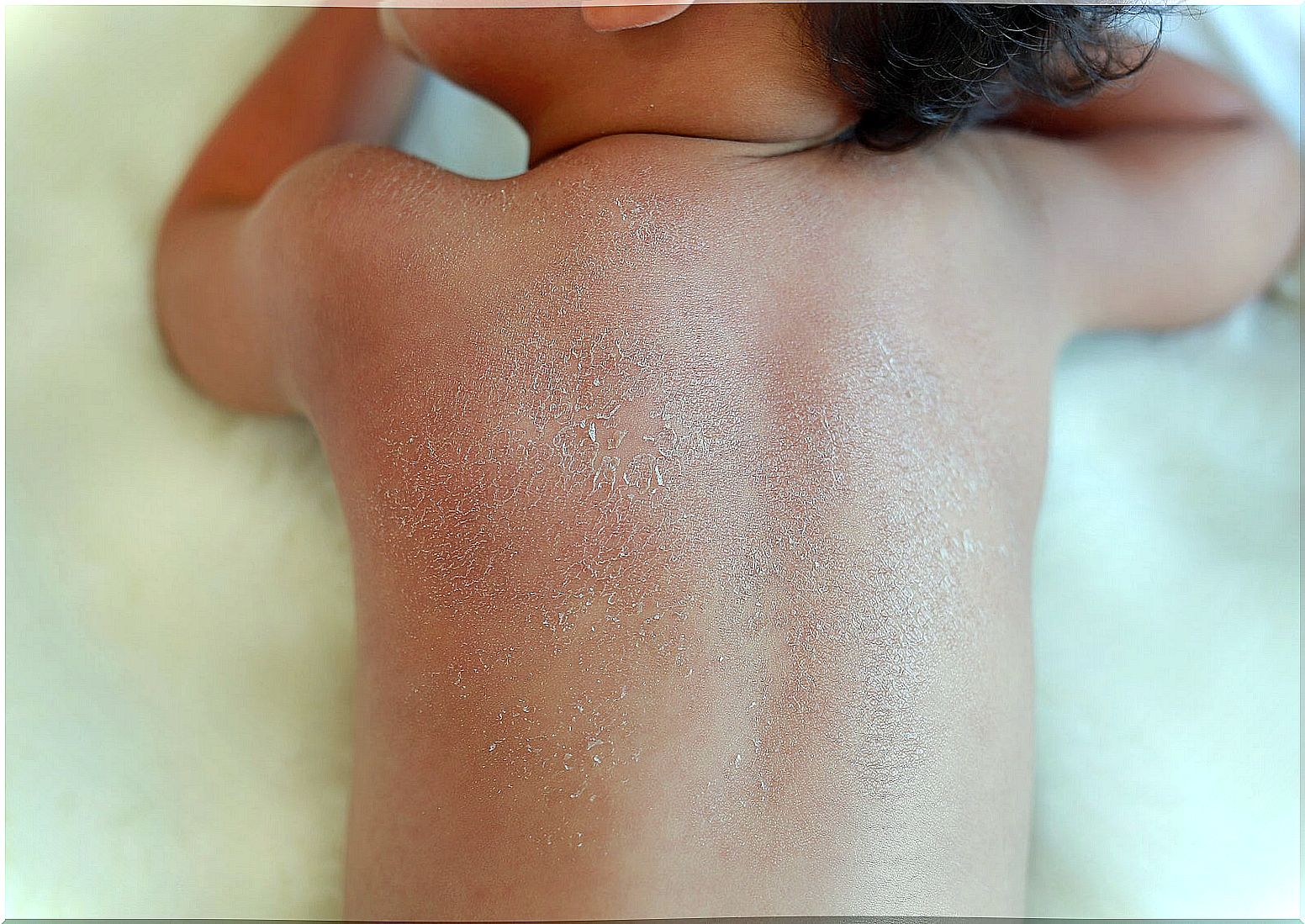
Dry skin or xerosis is a common manifestation in adults, although it also occurs in children. It is not contagious, nor is it serious, but it can cause discomfort in those who suffer from it. There are certain precautions and care to prevent this skin condition. Next, we tell you more about it.
Causes of dry skin in children
Children’s skin is delicate and sensitive, as it is not yet fully developed. The thickness of the epidermis and the stratum corneum is decreased in relation to that of adults.
Dehydrated skin is generated due to alterations in the skin barrier, where its high lipid composition is diminished.
Extreme temperatures
Dry skin occurs more frequently in the cold months. Both the dry air and the heating in the rooms cause the lack of oxygenation and vascularization of the dermis.

Constant moisturizing of the skin is recommended, with creams high in Vitamin A, Vitamin E, allantoin and associated. Likewise, humidifiers can be used in the rooms to increase the humidity levels in the spaces and contribute to the hydration of the skin.
Excessive and long baths
Constant baths with very hot water tend to eliminate the lipid layer that makes up the skin barrier. That is why this long-term routine causes the alteration of the protective function of the skin.
At the same time, the hygiene product used should be considered, because the vast majority of them have chemicals that deteriorate the lipid mantle. Consequently, the skin surface is exposed to being attacked by external agents or to trigger dermatological pathologies.
Diseases that occur with dry skin
Certain pathologies can present within their symptoms dry skin as a distinctive characteristic. Some of the diseases that occur with dry skin are the following:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Psoriasis.
- Ichthyosis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis.
- Perioral dermatitis.
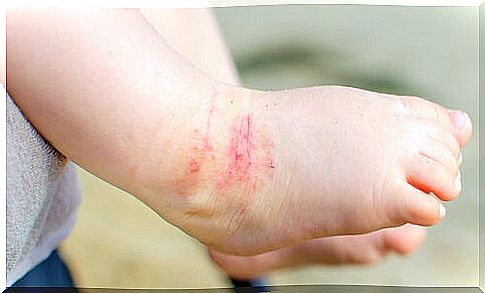
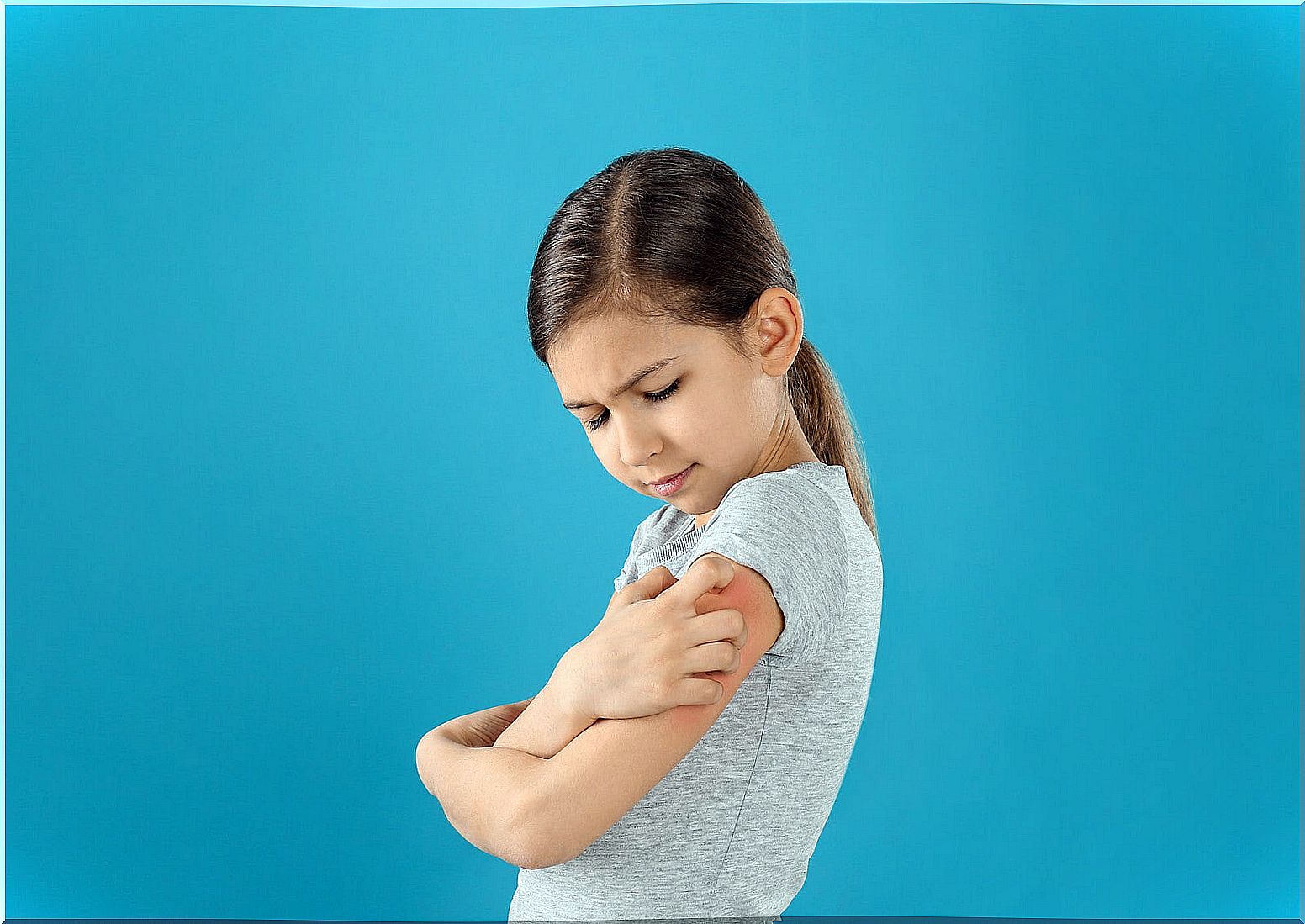
The main symptom of dry skin is intense itching of the skin surface. In turn, the more scratching there is, the more itching will be generated. Therefore, a vicious cycle of scratching or itching is generated that leads to excoriative lesions or eczema.
How to treat dry skin?
All dry skin is recommended to treat it because under these conditions it is more susceptible to injury by external agents. According to the indications of the American Academy of Dermatology Association , the treatment objectives would be the following:
- Eliminate symptoms (itching, pain or other).
- Recover the protective function of the skin surface.
- Teach the care measures to avoid dry skin.
Adequate humidification
Daily moisturizing of the skin is recommended with products containing urea, ceramides, Vitamin A, Vitamin E, glycerin, etc. Even one of the ideal times to apply it is within 5 minutes of bathing and skin hygiene.
It is there when the skin surface is more receptive to the products that are applied to it and its active ingredients act more efficiently.
Prolonged exposure to the sun can be a cause of dry skin. Consequently, today there are sunscreens with moisturizing agents in their formulas.
Bathrooms and hygiene
Hygiene is one of the essential steps to keep children’s skin barrier healthy and functional. In turn, the baths should be short and with warm water so as not to generate dehydration of the skin or predispose it to eczema or other pathologies.
The hygiene products used at the time of bathing must be chosen with criteria and being aware not to alter the pH of the skin’s surface.

A study in the Journal of Pediatrics concludes that syndet soaps (without detergents) are the most recommended to maintain the effectiveness of the skin barrier.
When should you go to a dermatologist?
Excessive dry skin can also be a sign of some other underlying pathology that exists in the body. The diagnosis will be made only through clinical observation in the medical consultation.
In the case of persisting with dry skin after having made the primary recommendations, a dermatologist should be consulted. A consultation with the specialist should also be made if there is an active lesion on the skin caused by scratching or if the itching persists.
Dry skin in children can be caused by atopic dermatitis. Therefore, if itching, xerosis, and the skin becomes reddened in the flexor areas of the body continue, the dermatologist can make such a diagnosis.