10 Types Of Dermatitis In Children
There are different types of dermatitis in children that lead parents to go to the doctor’s office anxious and with logical concern. However, the vast majority of these skin conditions are usually benign and not contagious.
Dermatitis is characterized by irritation of the skin surface, which may be accompanied by dry skin, itching, edema, redness, or other characteristic lesions.
Types of dermatitis in children
Children’s skin is more sensitive and delicate than that of adults due to its complete lack of development. For this reason, it is more vulnerable to certain external agents or to suffer from some skin diseases. Here are the most common types of dermatitis in children.
1. Psoriasis
In addition to the skin, psoriasis sometimes involves nail and joint involvement. Children with psoriasis are more prone to diabetes mellitus , obesity, juvenile arthritis, Crohn’s disease, obesity, and psychiatric disorders.
Plaques on the skin are erythematous, with overlapping white scales that most often develop on the scalp, flexure areas, and face. The scalp is often the first presentation site in children. In turn, the clinical manifestations have a symmetrical distribution and well-defined borders.
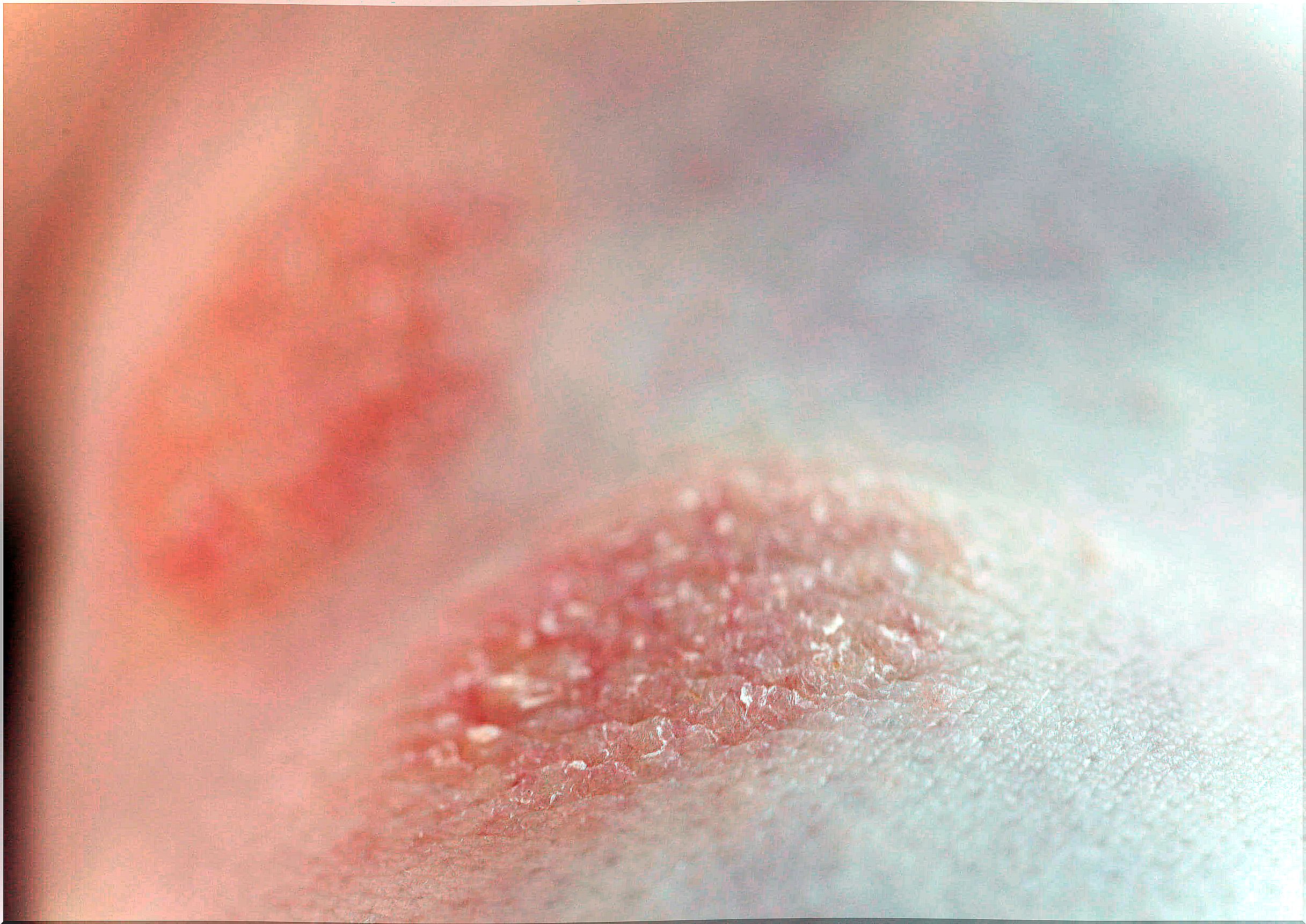
2. Dermatophytosis
Dermatophyte infection of the skin and adnexa is a common condition. In addition to the manifestations on the surface of the skin, it negatively affects the quality of life of those who suffer from it.
The lesions vary according to the type of dermatophyte that caused them and according to the host’s immune response. In turn, it can last for months or years and be asymptomatic or only itchy.
They are classified according to the location of the lesions:
- T. capitis (of the scalp).
- Tinea corporis.
- T. pedis (athlete’s foot).
- Tinea unguim.
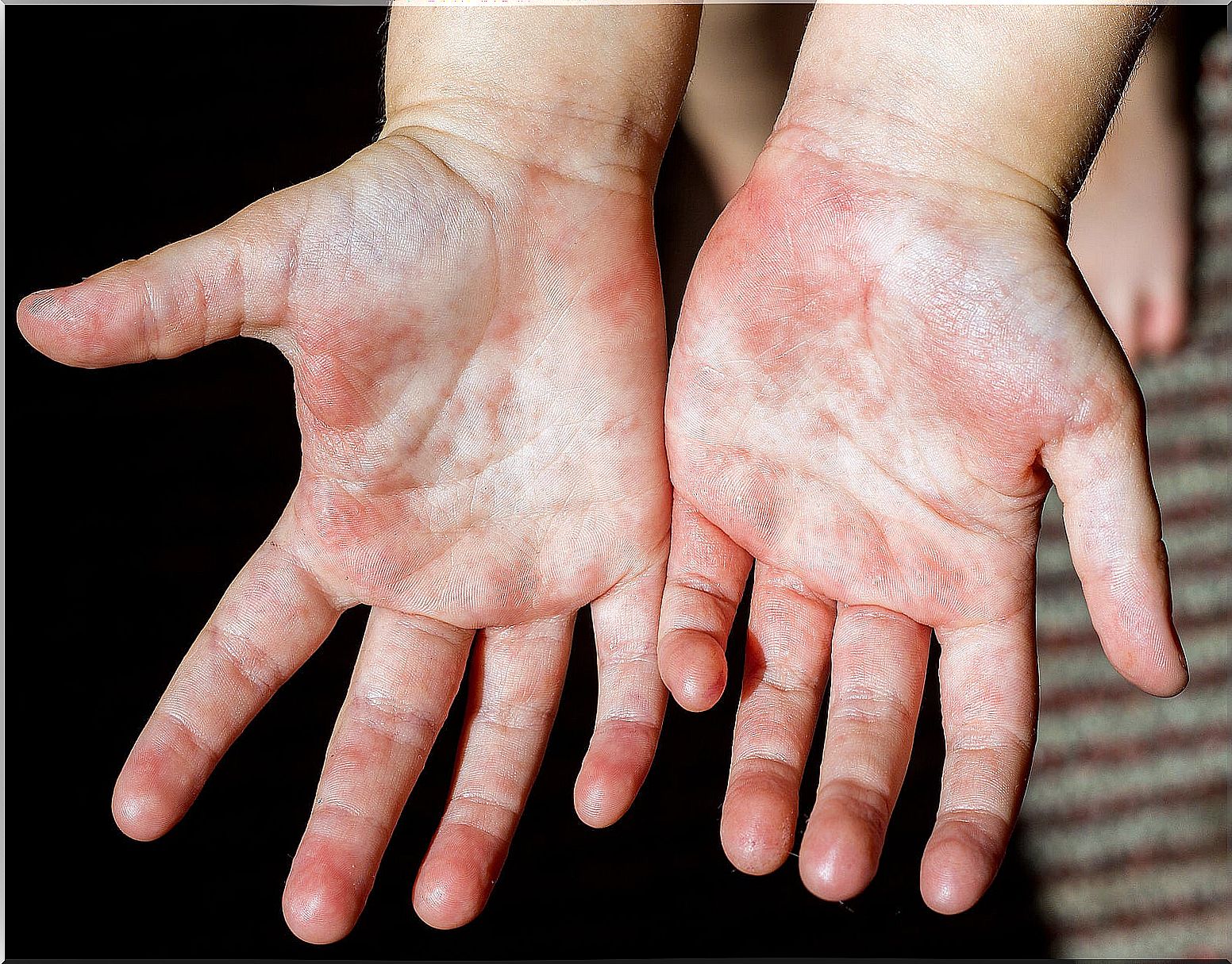
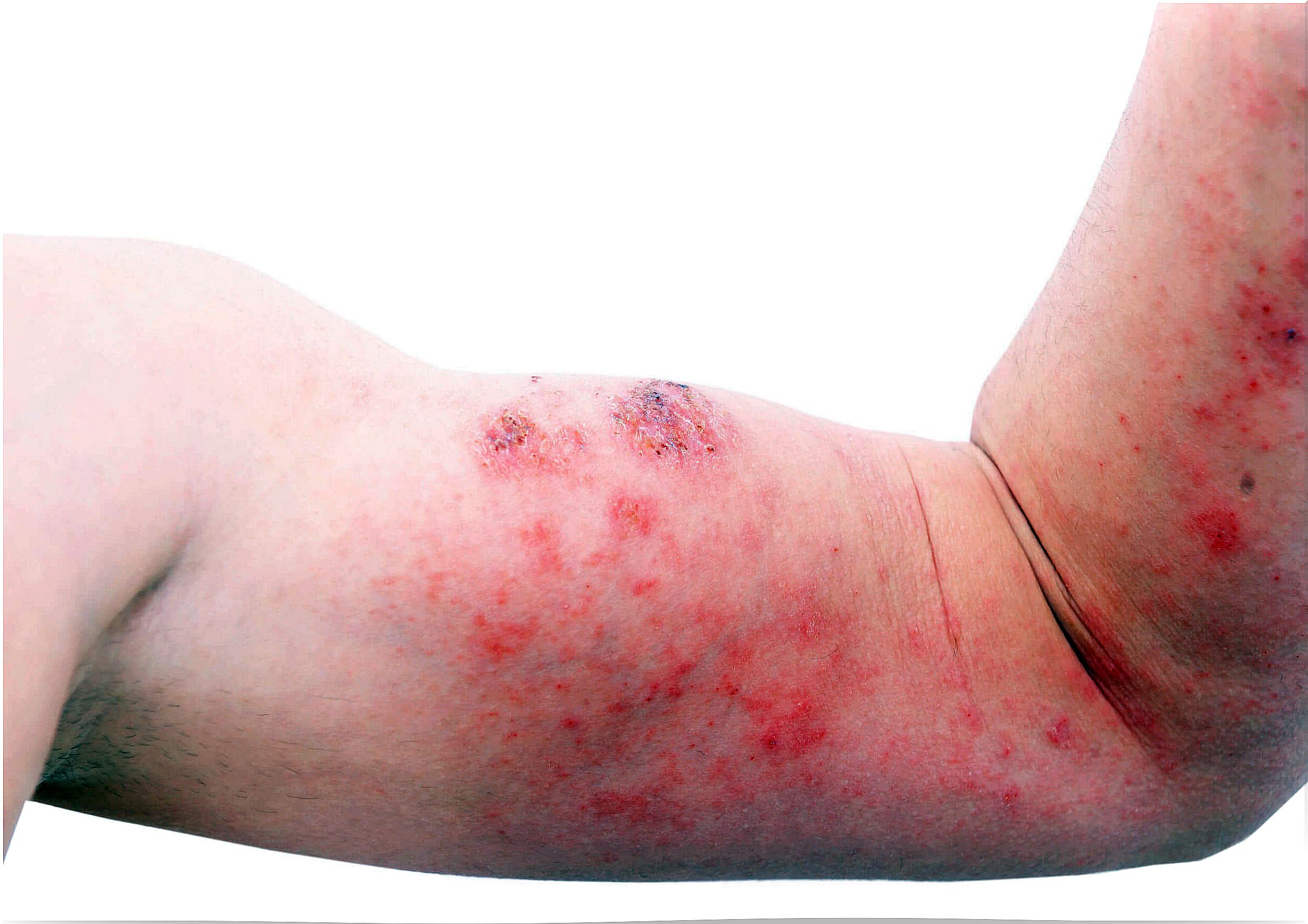
3. Atopic dermatitis, one of the most common types of dermatitis in children
Atopic dermatitis is the most common inflammatory skin disease. Its genesis involves genetic predisposition, the alteration suffered by the skin barrier and the dysregulation of the immune system.
It is a chronic disease that occurs with flare-ups and remissions. In turn, it is characterized by reddened skin, edematous, with an intense sensation of itching that leads to scratching and the subsequent presence of excoriation.
In infants, it is observed with greater predominance in places of flexion of the elbows and knees, as well as the wrists and ankles, although it can occur anywhere.
4. Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis in children is a common but underdiagnosed disease. In turn, it has allergic and irritant variants that must be ruled out with the differential diagnoses of atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, and infections.
The location of the injuries is related to the area of direct contact with the physical or chemical agents. In addition, the skin of children has a thinner epidermis compared to that of an adult, making it more vulnerable to allergic reactions.
Girls often have contact dermatitis reactions to perfumes found in certain products in the form of essential oils.
5. Pityriasis rosea Gibert
It is a benign papulosquamous disorder that resolves spontaneously. In most cases, it begins with a single large, erythematous, scaly plaque, called the heraldic plaque.
After the appearance of this plaque on the trunk or neck, a rash of multiple tiny lesions appears on the back of the back with a characteristic Christmas tree-like distribution.
Dermatitis may be preceded by the following symptoms:
- Fever.
- Arthralgias.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
- Sore throat.
6. Seborrheic dermatitis, another of the most common types of dermatitis in children
It is an inflammatory pathology of the skin that occurs in areas with the highest concentration of sebaceous glands, especially in the face, scalp and body folds. In turn, the rash is usually painless or itchy.
In most cases, childhood seborrheic dermatitis is mild and resolves on its own. It can even occur in newborns, in which it is called “cradle cap” .
7. Periorificial dermatitis
It is a benign rash characterized by the presence of tiny inflammatory papules and scaly pustules or plaques around the mouth, eyes, and nose. The diagnosis is made with the visual and clinical examination of the lesions. In this sense, a differential diagnosis should be made with acne vulgaris, rosacea, and sarcoidosis.
8. Scabies
Known as scabies, scabies is a contagious skin condition. It develops due to the infection of a mite, which is deposited inside the skin and causes intense itching predominantly at night.
Contagion occurs through skin-to-skin contact and transmission of fomites through clothing or sheets. Clinical manifestations include hyperkeratotic plaques that may be diffuse or localized on the soles, palms, and under the nails. Treatment of the affected child and all close contacts who have been with him are required.
9. Pityriasis versicolor
It is a superficial, benign and common fungal infection of the skin. Clinical features include hyperpigmented or hypopigmented fine scaling macules on the trunk, neck, and proximal extremities.
It is caused by a lipophilic fungus, which is a component of the normal skin flora. According to a review published in the Journal of Fungi , topical antifungal drugs are the first-line treatment for pityriasis versicolor.
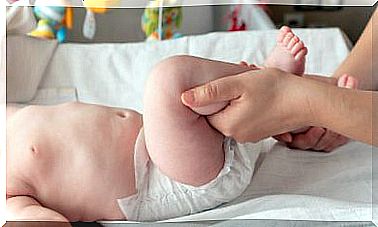
10. Diaper rash
It is an inflammatory reaction of the skin surface in the perianal and perineal regions. It develops due to irritation of the skin to different external agents such as urine, feces, humidity or other irritants such as detergents.
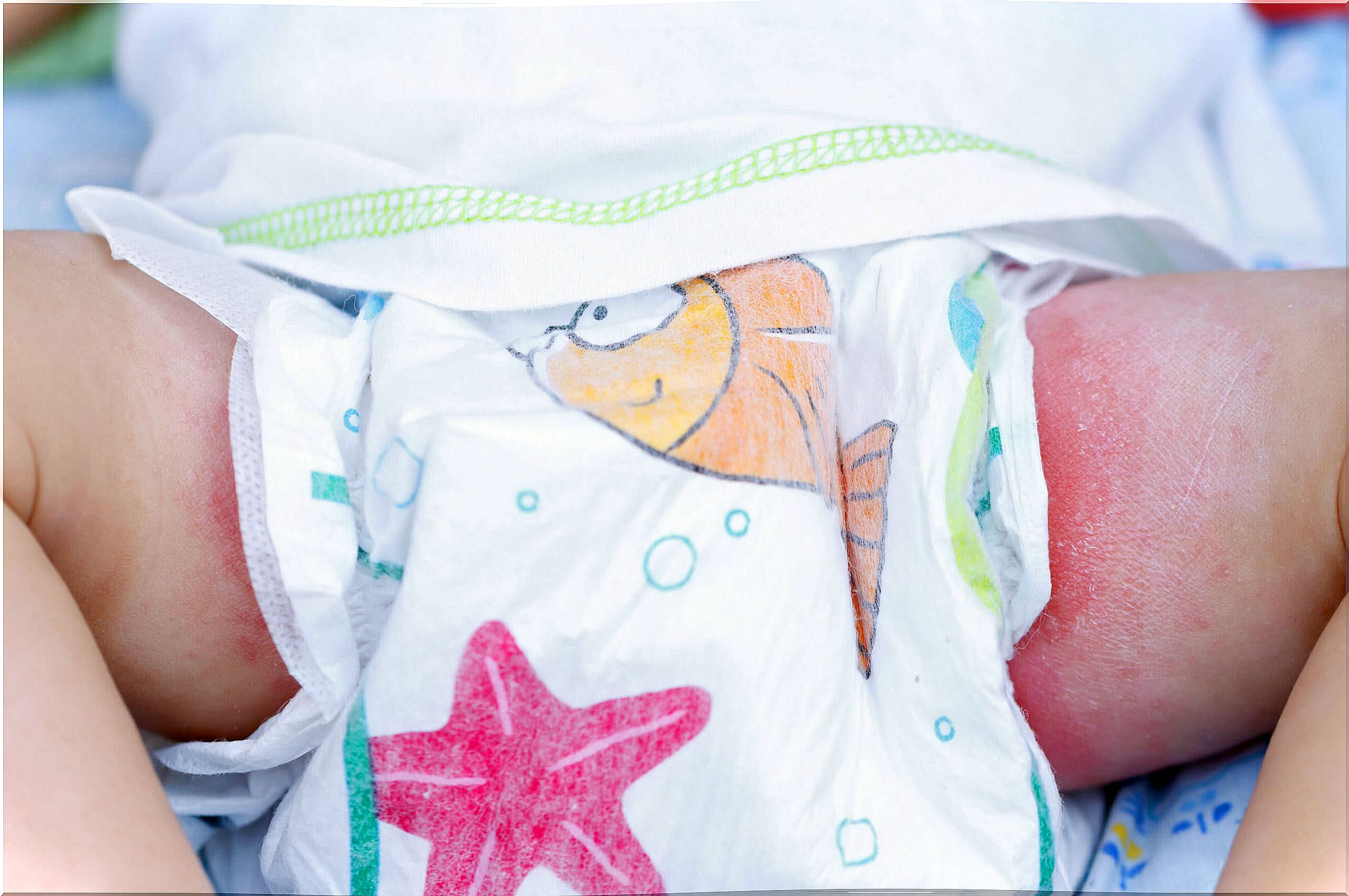
It is usually a mild and self-limited condition, however, on some occasions it can evolve into bacterial superinfections or Candida infections .
What to do with dermatitis in children?
Each dermatitis has its own management or specific therapeutic option. Therefore, before any sign or symptom that occurs, it is recommended to go to a dermatologist.
The specialist will be the one who makes the diagnosis and indicates the hygienic measures and treatment to begin to resolve the clinical picture. Although some dermatitis is self-healing, self- medication or the use of home remedies is not recommended.